Identification of a molecule (Arid5a) involved in the promotion of autoimmunity
Finding may contribute to potential therapeutics for treating IL-6–dependent diseases
Researchers at the Immunology Frontier Research Center (WPI- IFReC ), Osaka University, under the leadership of MASUDA Kazuya (researcher from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science) and KISHIMOTO Tadamitsu (Professor and former Osaka University President) have identified a molecule, Arid5a [AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5A], involved in the promotion of autoimmune diseases.
In the blood of patients with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the elevated levels of inflammatory cytokine 6 (IL-6) serum is observed. Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody Tocilizumab (trade name: Actemra ) has been approved in more than 90 nations and is used for treatment of autoimmune diseases. By blocking IL-6 signals, this antibody exerts a positive effect on many autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), juvenile idiopathic arthritis, Castleman's disease, scleroderma, and polymyalgia rheumatica, aortitis (Takayasu disease).
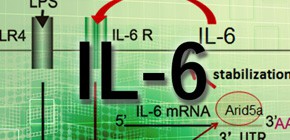
This group identified AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5A (Arid5a), a molecule that binds to the 3' untranslated region of IL-6 mRNA and inhibits destabilization of mRNA. This group demonstrated that a signal inducing the production of IL-6 also induced Arid5a and was involved in abnormal production of IL-6.
Additionally, this group also demonstrated that in Arid5a-defficient mice abnormal production of IL-6 was suppressed a finding which was consistent with the fact that Arid5a-deficient mice are resistant to EAE, an experimental model of human multiple sclerosis (MS).
Formerly, under the leadership of AKIRA Shizuo , Director, IFReC , a group of researchers discovered Regnase-1 , a molecule that destabilizes IL-6 mRNA. Arid5a identified by Dr. Kishimoto's group was found to inhibit the destabilizing effect of Regnase-1 in the the 3' untranslated region of IL-6 mRNA. Normally, Regnase-1 plays the role of degrading IL-6. It is thought that Arid5a inhibits the action of Regnase-1 and may be involved in abnormal production of IL-6 and develop autoimmune diseases.
The development of compounds to suppress Arid5a production or compounds to prevent Arid5a from binding to IL-6 mRNA will lead to the possible development of new therapeutics for inflammatory immune diseases attributable to abnormal levels of IL-6.
Abstract
Posttranscriptional regulation of IL-6 has been largely uncharacterized, with the exception of the ribonuclease Regnase-1, which prevents autoimmunity by destabilizing IL-6 mRNA. Here, we identified AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 5A (Arid5a) as a unique RNA binding protein, which stabilizes IL-6 but not TNF-α mRNA through binding to the 3′ untranslated region of IL-6 mRNA. Arid5a was enhanced in macrophages in response to LPS, IL-1β, and IL-6. Arid5a deficiency inhibited elevation of IL-6 serum level in LPS-treated mice and suppressed IL-6 levels and the development of T H 17 cells in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Importantly, Arid5a inhibited the destabilizing effect of Regnase-1 on IL-6 mRNA. These results indicate that Arid5a plays an important role in promotion of inflammatory processes and autoimmune diseases.

Figure 1
To learn more about this research, please read the full research report entitled " Arid5a controls IL-6mRNA stability, which contributes to elevation of IL-6 level in vivo " at this page of the PNAS website.
Related link :
