Discovery of Arid5a, a molecule that exasperates septic shock
Will lead to the inhibition of shock caused by bacterial infection
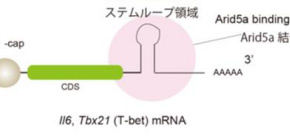
A research group of Tadamitsu Kishimoto (Immune Regulation, IFReC) revealed that one of the RNA-binding proteins, AT-rich interactive domain 5a (Arid5a) accelerates symptoms of septic shock. They previously found that Arid5a stabilizes IL-6 mRNA through its binding to IL-6 3’-untranslated region (UTR). In this study, they have shown that Arid5a promotes the production of γ-IFN in CD4+ T cells (Th1 cells) by stabilizing the mRNA of Tbx21 gene (encode T-bet), thereby exacerbating symptoms of sepsis. These results suggest that the neutralization of Arid5a function might lead to the treatment of septic shock as a therapeutic target. So far, there is no critical way of treatment for sepsis, with which the mortality is about 30 %.
Abstract
Adenine-thymine (AT)-rich interactive domain containing protein 5a (Arid5a) is an RNA-binding protein that has been shown to play an important immune regulatory function via the stabilization of IL-6 and STAT3 mRNA. However, the role of Arid5a in the overwhelming and uncontrolled immune response that leads to septic shock is unknown. Here, we report that Arid5a-deficient mice are highly resistant to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock and secrete lower levels of major proinflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-6, and TNF-α, than WT mice in response to LPS. Arid5a deficiency resulted in decreased levels of IFN-γ under Th1 cell conditions, in which T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet) mRNA expression was inhibited. Arid5a bound to the conserved stem loop structure of the 3′UTR of T-bet and stabilized its mRNA. Arid5a-deficient mice were also resistant to Propionibacterium acnes-primed LPS injection, which is considered to be a T-cell–mediated IFN-γ dependent endotoxic shock mouse model. Thus, regulation of IFN-γ by Arid5a via the stabilization of T-bet mRNA in Th1 cells contributes to the development of septic shock in mice. In addition, our previous study suggests that Arid5a control the IL-6 level in vivo in response to LPS by stabilization of IL-6 mRNA. We also observed that neutralization of IFN-γ and IL-6 significantly recovered the mice from endotoxic shock. Taken together, we conclude that Arid5a regulates the augmentation of IL-6 and IFN-γ in response to LPS, which possibly works synergistically for amplification of various other cytokines that ultimately cause the development of septic shock in mice.
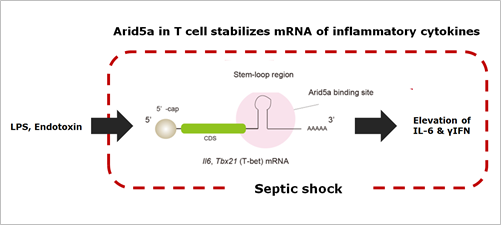
Figure 1. Elevation of inflammatory cytokines caused by Arid5a after the endotoxin shock
Figure 2. Survival rate for Arid5a KO mice and WT mice after LPS injection
To learn more about this research, please view the full research report entitled “ Arid5a exacerbates symptoms of Septic shock ” at this page of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the USA (PNAS) website.
Related link
