Technology for increasing the strength of parts and achieving metal coating of fine parts developed
Will facilitate applications to machined parts necessary for aviation, space, and oil drilling industries
A group of researchers led by Associate Professor TSUKAMOTO Masahiro, Joining and Welding Research Institute, Osaka University, developed Multi-laser Metal Deposition (M-LMD) technology, which makes it easy to control the use of metallic powder and lasers, and is appropriate for additive manufacturing (AM), AM of thin plates, and AM on a 5-axis machining center.
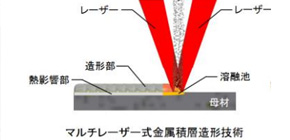
In conventional laser metal deposition (LMD) technology, a laser beam from the center of the laser machining head forms a molten pool on the component surface and metallic powder supplied to the pool from the laser beam surrounding area builds up the molten metal layer by layer. However, it was a problem that metallic powder was not efficiently supplied to the molten pool because powder fed from the machining head was fine and light. In addition, in LMD technology, in the case of thin parent material, the material itself might be heat-affected by melting.
A group of researchers led by Associate Professor Tsukamoto developed an AM processing head, achieving a structure in which multiple laser beams were irradiated from a machining head toward a light focusing point and powder material was fed from the machining head. In this technology, the position of the laser beam and the opening for supplying metallic powder is opposite to that of conventional LMD technology. This structure made it possible for metallic powder fed from the machining head center to be melted before it reached the parent material by laser, which reduced thermal effects to the parent material as much as possible, enabling additive manufacturing with high efficiency and precision.
In M-LMD technology developed by this joint group, thanks to a simple structure having an only one metallic powder feed, even when the AM machining head is rotated, metallic powder is less affected by changes in the direction of gravity, making stable supply of metallic powder to the processing point possible. Compared to conventional technologies, it has become easier to control the use of metallic powder and laser, and AM on a 5-axis machining center has become available through the installation of this machining head.
This group’s achievement will lead to the application to machined parts necessary for aviation, space, and oil drilling industries, including application to metallic coating, which increases the strength and durability of parts, partial repair of expensive parts, and partial additive manufacturing of microstructural portions.
M-LMD technology was installed on machining tools by Yamazaki Mazak Corporation, a world first, and was presented in the 28th Japan International Machine Tool Fair (JIMTOF) which was held at Tokyo Big Sight from Thursday, November 17 through Tuesday, November 22, 2016.
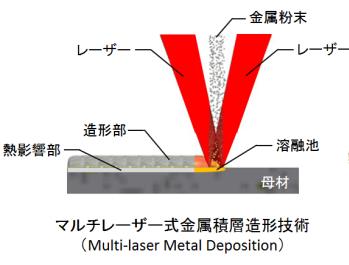
Figure 1. Multi-laser Metal Deposition

Figure 2. AM machining head
Related link
