Key findings to develop a vaccine against Toxoplasma
Identified the role of an experimental pathogenic parasite toxoplasma-inactivated vaccine
Toxoplasma gondii is a common parasite which causes the development of fatal encephalosis or pneumonia in immunodeficient patients under treatment of AIDS or cancer. Pregnant women who are infected may suffer a miscarriage or the newborn child may suffer from a congenital disease. Currently, a toxoplasma vaccine for humans is not available. Using experimental animals such as mice, basic research for developing an inactivated vaccine is underway.
A group of researchers led by Masahiro Yamamoto, Professor at Research Institute for Microbial Diseases and the Immunology Frontier Research Center, Osaka University found that p62, a host molecule, played an important role in exerting immune effects of an experimental pathogenic parasite toxoplasma-inactivated vaccine. This group’s achievement is expected to offer strategies for developing a toxoplasma-inactivated vaccine targeting p62 for treating toxoplasmosis, whose case reports have been on the rise in Japan in recent years.
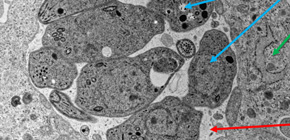
From an prior study which found that the antigens derived from the toxoplasma emitted within the parasitophorous vacuole become the major antigens for the killer T cells, Professor Yamamoto’s group investigated the activation of killer T cells when the toxoplasma-infected cells were stimulated by interferon-γ (IFN-γ). As a result, it was found that the activity of antigen-specific killer T cells in infected cells that were stimulated by IFN-γ was dramatically higher than in non-stimulated infected cells. This robust activation of killer T cells seen when these infected cells undergo IFN-γ stimulation was significantly reduced in mice with p62 deficiencies. Even on an individual level, when compared with wild-type mice, there was a sharp decrease in antigen-specific killer T cells in p62 deficient mice when administered the toxoplasma-inactivated vaccine.
These findings clarified that IFN-γ-dependent p62 has the unique role of gathering in the parasitophorous vacuole of toxoplasma through IFN-γ stimulation and activating the antigen-specific killer T cells released within the parasitophorous vacuole, a world first.
The results of this research was published in Cell Reports on Friday, 2 October 2015.
Abstract
p62 (also known as Sqstm1) is a selective autophagy adaptor with an ubiquitin-binding domain. However, the role of p62 in the host defense against Toxoplasma gondii infection is unclear. Here, we show that interferon γ (IFN-γ) stimulates ubiquitin and p62 recruitment to T. gondii parasitophorous vacuoles (PVs). Some essential autophagy-related proteins, but not all, are required for this recruitment. Regardless of normal IFN-γ-induced T. gondii clearance activity and ubiquitination, p62 deficiency in antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and mice diminishes the robust IFN-γ-primed activation of CD8+ T cells that recognize the T. gondii-derived antigen secreted into PVs. Because the expression of Atg3 and Irgm1/m3 in APCs is essential for PV disruption, ubiquitin and p62 recruitment, and vacuolar-antigen-specific CD8+ T cell activation, IFN-γ-mediated ubiquitination and the subsequent recruitment of p62 to T. gondii are specifically required for the acquired immune response after PV disruption by IFN-γ-inducible GTPases.
To learn more about this research, please view the full research report entitled “ p62 plays a specific role in interferon- γ -induced presentation of a Toxoplasma vacuolar antigen ” at this page of the Cell Reports website.
Related link
