New insulin compound could improve therapy for diabetes patients
In a promising discovery that could improve the clinical delivery of insulin for people living with diabetes, scientists have developed a non-fibrillating form of human insulin.
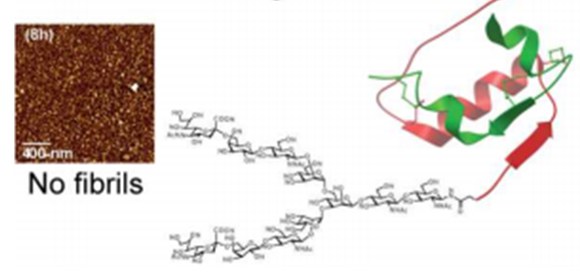
Using a novel glycosylation technique, an international research team led by Associate Professor Akhter Hossain from the Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, has successfully synthesised an insulin analogue called glycoinsulin that demonstrates the same glucose-lowering effects as native insulin in preclinical studies without fibril formation.
Fibrils can arise when insulin compounds aggregate together forming clumps. For diabetic patients who rely on pump infusions to administer insulin, fibrils pose serious risk in blocking the delivery of insulin which can potentially lead to life threatening under-dosing.
Associate Professor Hossain said that the discovery of glycoinsulin presents a promising solution for patients.
“Not only did our research demonstrate that glycoinsulin does not form fibrils, even at high temperature and concentration, but also that it is more stable in human serum than native insulin. Together these findings could position glycoinsulin as an excellent candidate for use in insulin pumps and a way to improve the shelf life of insulin products,” said A/Prof Hossain.
"We hope now to streamline the manufacturing process for glycoinsulin so that this molecule can continue to be further investigated in larger studies."
In what can cause significant patient burden and medicine wastage, insulin pump infusion sets are required to be replaced every 24 hours to 72 hours to mitigate the occurrence of fibrils. In the USA alone, more than US$1 billion could be saved per year if the usage period for insulin increased from two to six days.
Globally, one in 11 people live with diabetes. 1 It is the fastest growing chronic disease. Insulin pumps are used as part of diabetes management for around 15,000 people in Australia and 350,000 people in the United States. 2 , 3
Critical to the success of the study was the engineering of an insulin-sugar complex from egg yolks using a method jointly developed by collaborators, Associate Professor Ryo Okamoto and Professor Yasuhiro Kajihara, from Osaka University, Japan.
Professor John Wade from the Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health who co-led the research commented on the landmark success of the research.
“Typically, the chemical modification of insulin causes structural destabilisation and inactivation, but we were able to successfully synthesise glycoinsulin in a way that retains its insulin-like helical structure. The result is an almost fully active insulin analogue which has demonstrated near-native binding to insulin receptors in both lab and animal studies.”
The research was funded by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. It has been published in the Journal of American Chemical Society : doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b11424 .
1 Diabetes Australia, Diabetes Globally, https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/diabetes-globally
2 Brooke H., et al. An Overview of Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors for the Generalist. J. Clin Med 2016; 5(1):5 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4730130/
3 Diabetes Australia, Insulin Pump Therapy in Australia, https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/news/13542?type=articles
Related links
