Important factor to control the size of “trash bags” of the cell discovered
A group of scientists from Osaka University and Kyoto Sangyo University has discovered a protein responsible for the determination of the size of double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes, which deliver cytoplasmic materials to the lytic compartment of the cell for degradation via autophagy.
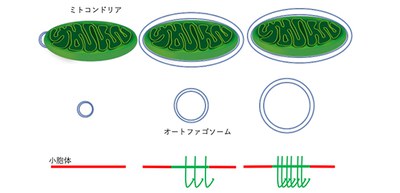
Autophagy is the natural self-cleaning system to remove damaged cells in order to regenerate newer, healthier cells and is conserved throughout the eukaryotes, including humans. Autophagy is mediated by an organelle called autophagosome. Autophagosomes engulf a variety of targets with diverse sizes from portions of cytosol to larger organelles and deliver them for lysosomal degradation. When enwrapping a protein in a cell, autophagosomes are mostly uniform in size (1μm in diameter), but when enclosing mitochondria larger than the protein, autophagosomes become larger.
Living things are characterized by hierarchical organization and living organisms in each hierarchical level are limited in size. Height in humans takes on any number of values within a certain range and organs have their own autonomous sizes. However, what determines the size of organelles, including autophagosomes, is not well understood.
In this study, the research group focused on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane protein, ERdj8. ERdj8 is the novel eighth member of the ERdj family that plays an important role in lipid synthesis as well as protein folding and protein maturation in the ER.
Observation using structured illumination microscopy revealed that ERdj8 was localized mainly in a specialized subdomain of the ER where ERdj8 primarily resides. While overexpression of ERdj8 increased the size of autophagosomes, ERdj8 ablation resulted in a defect in engulfing larger targets. ERdj8 depletion allowed enwrapping of small paternal mitochondria, but not normal somatic mitochondria, large protein aggregates, and latex beads of 3μm in diameter. This showed that ERdj8 in an ER subdomain involved in autophagosome formation affected the size of the autophagosome membrane.
It is thought that the magnitude of autophagosome formation is strictly regulated because the role of autophagy is the inevitable degradation of cytosolic components and excessive or uncontrolled levels of autophagy induces cell death. On the other hand, the increase and decrease in size and number of autophagosomes are closely related to the pathogenesis of various diseases, such as cancer and neurodegeneration.
This study showed the possibility that ERdj8 may play a critical role in fine-tuning the autophagosome formation process and will lead to the research and development for autophagy-related diseases.
Figure 1
The article, “ERdj8 governs the size of autophagosomes during the formation proces,” was published in Journal of Cell Biology at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201903127.
Related Links
Center for Frontier Oral Science, Gradate School of Dentistry, Osaka University
(link in Japanese)
