Modulation mechanism of chromosome segregation clarified
A group of researchers from Osaka University clarified how centromere protein C (CENP-C) binds to kinetochore complexes.
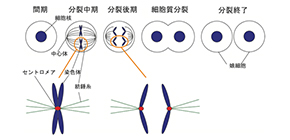
A genome, the genetic material of an organism, is stored in long molecules of DNA called chromosomes. Accurate transmission of chromosomes during meiosis is necessary for maintaining life. An error in the transmission of chromosomes results in chromosomal structural abnormalities, causing many disorders, such as cancer and Down syndrome.
During cell division, kinetochores assemble at the site of centromeric chromatin on each chromosome to bind spindle microtubules and promote chromosome segregation. Thus, the formation of kinetochore is essential for mitosis.
For proper assembly of the kinetochore structure, it is crucial that CENP-C binds to the centromere on the chromosome; however, its mechanism was not well-known.
The centromere binding to CENP-C occurs during mitosis. Since CENP-C is phosphorylated during mitosis, the researchers examined the phosphorylation in CENP-C, identifying a conserved threonine residue in CENP-C as a key CDK1-phosphorylation site. Mutants lacking the CENP-C motif did not localize on the centromere.
The binding of recombinant CENP-C (phosphorylated or unphosphorylated) to the CENP-A nucleosome was comparable to that of phosphorylated CENP-C, showing that phosphorylation of CENP-C facilitates its binding to CENP-A in vitro. The researchers also examined the significance of CDK1-mediated phosphorylation of CENP-C during mitosis in human and chicken cells, finding that phosphorylation of CENP-C facilitates its binding to CENP-A in vitro and in vivo.
Controlling cell division and chromosomal division is crucial for understanding causes of cancer and Down syndrome, which are caused by genomic instability, and developing anticancer drugs. Phosphorylation of CENP-C may become a new target for anticancer drugs. This group’s achievements will mark the beginning of development of new anticancer drugs.
Figure 1
Figure 2
The article, “CDK1-mediated CENP-C phosphorylation modulates CENP-A binding and mitotic kinetochore localization,” was published in Journal of Cell Biology at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201907006 .
