A function of the chromosomal terminus vital for human health discovered
Protein “Shugoshin” maintains proper gene expression
In cooperation with the Graduate School of Science, Graduate School of Frontier Biosciences, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, and the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences at Tokyo University, a group of researchers led by KANOH Junko (Associate Professor, Laboratory of Signal Networks for Life Maintenance, Institute for Protein Research, Osaka University), elucidated a function of the chromosomal terminus.
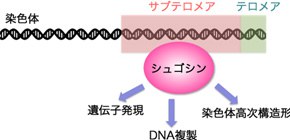
Specifically, this group found that a protein called Shugoshin binds with subtelomeres, the telomere-adjacent regions and that through which the proper gene expression in subtelomeres is maintained. Telomere is known to play a vital role.
This group also clarified that Shugoshin controls DNA replication (the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division) in subtelomeres as well as higher-order structure of chromosomes.
The clarification of the mystery of whether Shugoshin controls the subtelomeres or similar control systems work in humans as well will lead to the elucidation of a mechanism for developing abnormal telomere structure such as multiple malformation and mental retardation.
Abstract
A chromosome is composed of structurally and functionally distinct domains. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the formation of chromatin structure and the function of subtelomeres, the telomere-adjacent regions, remain obscure. Here we report the roles of the conserved centromeric protein Shugoshin 2 (Sgo2) in defining chromatin structure and functions of the subtelomeres in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. We show that Sgo2 localizes at the subtelomeres preferentially during G 2 phase and is essential for the formation of a highly condensed subtelomeric chromatin body ‘knob’. Furthermore, the absence of Sgo2 leads to the derepression of the subtelomeric genes and premature DNA replication at the subtelomeric late origins. Thus, the subtelomeric specialized chromatin domain organized by Sgo2 represses both transcription and replication to ensure proper gene expression and replication timing.

To learn more about this research, please view the full research report entitled " Shugoshin forms a specialized chromatin domain at subtelomeres that regulates transcription and replication timing " at this page of the Nature Communications website.
Related link
