Discovery of RNA cleavage enzyme involved in RNA-editing
possible step in development of therapeutic agents for mental disorders
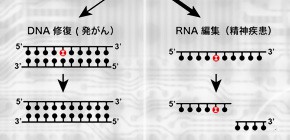
Under the leadership of KURAOKA Isao ( Associate Professor, Graduate School of Engineering Science, Osaka University), a group of researchers identified a protein involved in DNA damage, Human Endonuclease V (hEndoV), and clarified that hEndoV acted as an i-RNase, RNA cleavage enzyme involved in RNA-editing.
DNA repair protein hEndoV was thought capable of repairing inosine from damaged DNA. Research showed that inosine occurred spontaneously and caused mutations with a high frequency. Moreover, it had been reported that mice lacking this protein developed cancer at an increased rate.
This group purified hEndoV and found that hEndoV clove inosine-containing RNA (i-RNA) as an I-RNase and deactivated RNA editing.
RNA editing frequently occurs in the human brain and it is known that RNA editing is associated with mental conditions such as schizophrenia and depression. This group's research demonstrated that hEndoV is a key factor determining the fate of i-RNA. Thus, research into i-RNase activity may lead to the development of therapeutic agents for certain mental disorders.
Abstract
Deamination of DNA bases can create missense mutations predisposing humans to cancer and also interfere with other basic molecular genetic processes; this deamination generates deoxyinosine from deoxyadenosine. In Escherichia coli, the highly conserved endonuclease V is involved in alternative excision repair that removes deoxyinosine from DNA. However, its exact activities and roles in humans are unknown. Here we characterize the FLJ35220 protein, the human homologue of E. coli endonuclease V, hEndoV as a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA. hEndoV preferentially binds to RNA and efficiently hydrolyses the second phosphodiester bond located 3′ to the inosine in unpaired inosine-containing ssRNA regions in dsRNA. It localizes to the cytoplasm in cells. The ribonuclease activity is promoted by Tudor staphylococcal nuclease and detected on inosine-containing dsRNA created by the action of adenosine deaminases acting on RNA. These results demonstrate that hEndoV controls the fate of inosine-containing RNA in humans.

To learn more about this research, please read the full research report entitled " Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA " at this page of the Nature Communications website.
Related link :
