Protein to Regulate Cell Migration Identified
Mechanisms of anti-atherogenic action and anticancer effect via augmented AMP-activated protein kinase activity clarified
A group of researchers led by TSUKAMOTO Osamu , Assistant Professor, Medical Chemistry, Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University identified Pdlim5, a protein which becomes phosphorylated by augmented AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity and regulates cell migration. That is, this group has clarified a part of the mechanisms of anti-atherogenic action and anticancer effect via augmented AMPK activity.
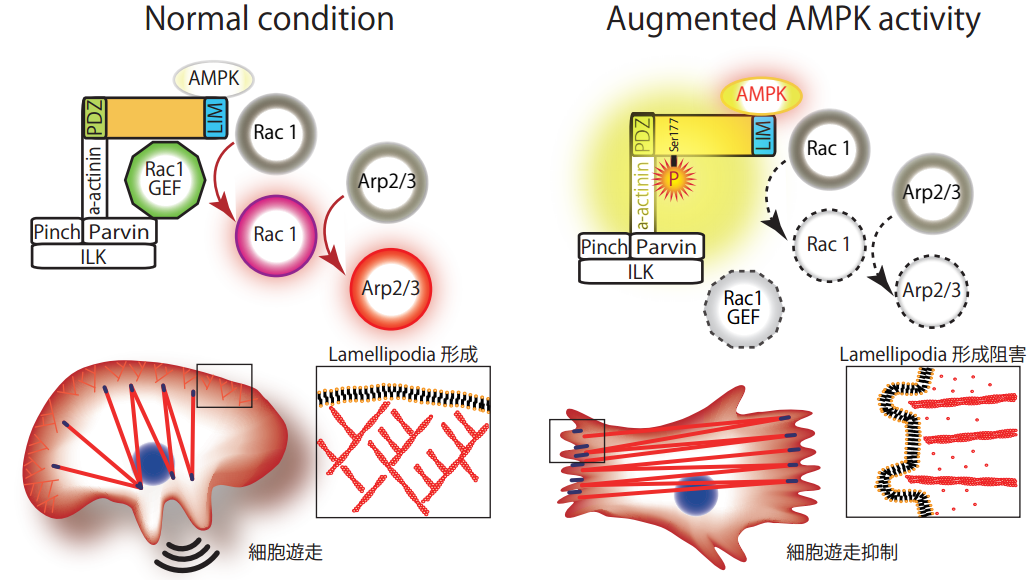
Phosphorylation of Pdlim5 at Ser177 by AMPK inhibits formation of lamellipodia and regulates cell migration. The elucidation of how progression of arterial sclerosis as well as progression and metastasis of cancer are suppressed by augmentation of AMPK activity and its clinical application is sought after.
Abstract
Augmented AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity inhibits cell migration, possibly contributing to the clinical benefits of chemical AMPK activators in preventing atherosclerosis, vascular remodelling and cancer metastasis. However, the underlying mechanisms remain largely unknown. Here we identify PDZ and LIM domain 5 (Pdlim5) as a novel AMPK substrate and show that it plays a critical role in the inhibition of cell migration. AMPK directly phosphorylates Pdlim5 at Ser177. Exogenous expression of phosphomimetic S177D-Pdlim5 inhibits cell migration and attenuates lamellipodia formation. Consistent with this observation, S177D-Pdlim5 suppresses Rac1 activity at the cell periphery and displaces the Arp2/3 complex from the leading edge. Notably, S177D-Pdlim5, but not WT-Pdlim5, attenuates the association with Rac1-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors at the cell periphery. Taken together, our findings indicate that phosphorylation of Pdlim5 on Ser177 by AMPK mediates inhibition of cell migration by suppressing the Rac1-Arp2/3 signalling pathway.
To learn more about this research, please view the full research report entitled " Augmented AMPK activity inhibits cell migration by phosphorylating the novel substrate Pdlim5 " at this page of the Nature Communications website.
Related Link
