The fork in the road to DNA repair
Japanese researchers from Osaka University have uncovered a way in which our cells regulate the repair of broken DNA. Their results, published in the journal “Cell Reports” for , show a common molecule regulates multiple repair mechanisms and help shed light on how the cell maintains the integrity of the human genome when it is damaged.
The human body consists of trillions of cells, and within each are billions of DNA molecules. Strict maintenance of the molecules is essential to maintain a healthy cell and thus a healthy body.
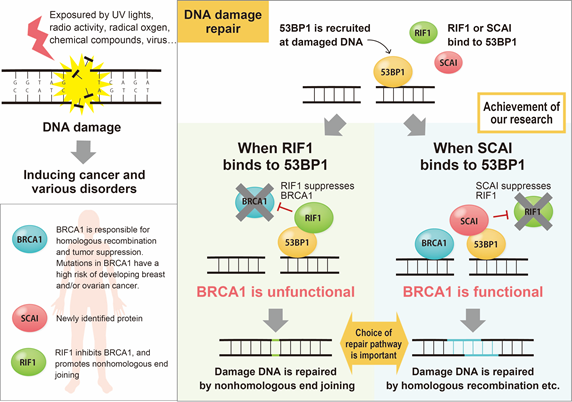
This maintenance is challenged by the daily bombardment of chemicals, UV light, radical oxygen and radiation that can damage the DNA molecules. If left unrepaired, the damage could lead to genomic instability and cell death. Thankfully, evolution has created in the cell innate repair mechanisms to fix any damaged DNA.
"The two mechanisms in the cell are non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination (HR) for repairing DNA double strand break" explains Chikashi Obuse, Professor at the Osaka University Graduate School of Sciences.
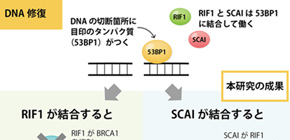
While NHEJ and HR both function to repair damaged DNA, they respond to different situations; types of damage, presence or absence of homologous template or cell cycle stages etc. What has continued to elude researchers is how the cell knows which system to call. Obuse shows in his latest report that the protein suppressor of cancer cell invasion (SCAI) plays an important role for the selection of HR.
To study the function of SCAI, Obuse and his team of scientists exposed human cells to X-ray irradiation to damage the DNA.
"Our results suggested SCAI bound to 53BP1 to promote the recruitment of HR proteins. When we depleted SCAI these proteins did not accumulate," he said.
In particular, Obuse highlighted the great diminishment of the protein BRCA1 at damage sites when SCAI was depleted. On the other hand, SCAI presence inhibited another protein, RIF1, to promote the recruitment of BRCA1.
"RIF1 is known to inhibit BRCA1 accumulation at DNA damaged sites. It binds to 53BP1. When we looked at confocal imaging of cells, we saw RIF1 initially accumulated at sites of DNA damage but was gradually replaced by SCAI," said Obuse.
This led the scientists to wonder if SCAI and RIF1 competed to bind to 53BP1 and whether this binding determined the DNA repair mechanism.
Indeed, additional experiments showed that the phosphorylation state of 53BP1 determined its binding partner.
"The next question for us is to determine which upstream kinases are responsible for phosphorylating the sites of 53BP1 needed for binding with SCAI," added Obuse. "The upstream signaling molecules will be important for helping to determine the cell's choice for either the NHEJ or HR pathway."
Abstract
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired by either the homology-directed repair (HDR) or the non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) pathway. RIF1 (RAP1-interacting factor homolog) was recently shown to stimulate NHEJ through an interaction with 53BP1 (p53-binding protein 1) phosphorylated at S/TQ sites, but the molecular mechanism underlying pathway choice remains unclear. Here, we show that SCAI (suppressor of cancer cell invasion) binds to 53BP1 phosphorylated at S/TP sites and facilitates HDR. Upon DNA damage, RIF1 immediately accumulates at damage sites and then gradually dissociates from 53BP1 and is subsequently replaced with SCAI. Depletion of SCAI reduces both the accumulation of HDR factors, including BRCA1 (breast cancer susceptibility gene 1), at damage sites and the efficiency of HDR, as detected by a reporter assay system. These data suggest that SCAI inhibits RIF1 function to allow BRCA1-mediated repair, which possibly includes alt-NHEJ and resection-dependent NHEJ in G1, as well as HDR in S/G2.
To learn more about this research, please view the full research report entitled “ Inhibition of RIF1 by SCAI Allows BRCA1-Mediated Repair ” at this page of the Cell Reports website.
Related links
