Clarification of the architecture of the flagellar apparatus in the fast-swimming magnetotactic bacterium MO-1
Under the leadership of Juanfan Ruan , Researcher, KATO Takayuki , Assistant Professor, and NAMBA Keiichi , Professor, Graduate School of Frontier Biosciences, Osaka University, and Long-Fei Wu , Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), [ French National Centre for Scientific Research], a group of researchers, using cryo-electron tomography, have clarified the way in which the flagellar apparatus in the fast-swimming magnetotactic bacterium MO-1 is constructed.
Abstract
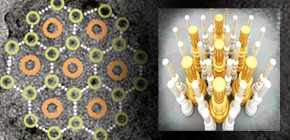
The bacterial flagellum is a motility organelle that consists of a rotary motor and a helical propeller. The flagella usually work individually or by forming a loose bundle to produce thrust. However, the flagellar apparatus of marine bacterium MO-1 is a tight bundle of seven flagellar filaments enveloped in a sheath, and it has been a mystery as to how the flagella rotate smoothly in coordination. Here we have used electron cryotomography to visualize the 3D architecture of the sheathed flagella. The seven filaments are enveloped with 24 fibrils in the sheath, and their basal bodies are arranged in an intertwined hexagonal array similar to the thick and thin filaments of vertebrate skeletal muscles. This complex and exquisite architecture strongly suggests that the fibrils counter- rotate between flagella in direct contact to minimize the friction of high-speed rotation of individual flagella in the tight bundle within the sheath to enable MO-1 cells to swim at about 300 μm/s.
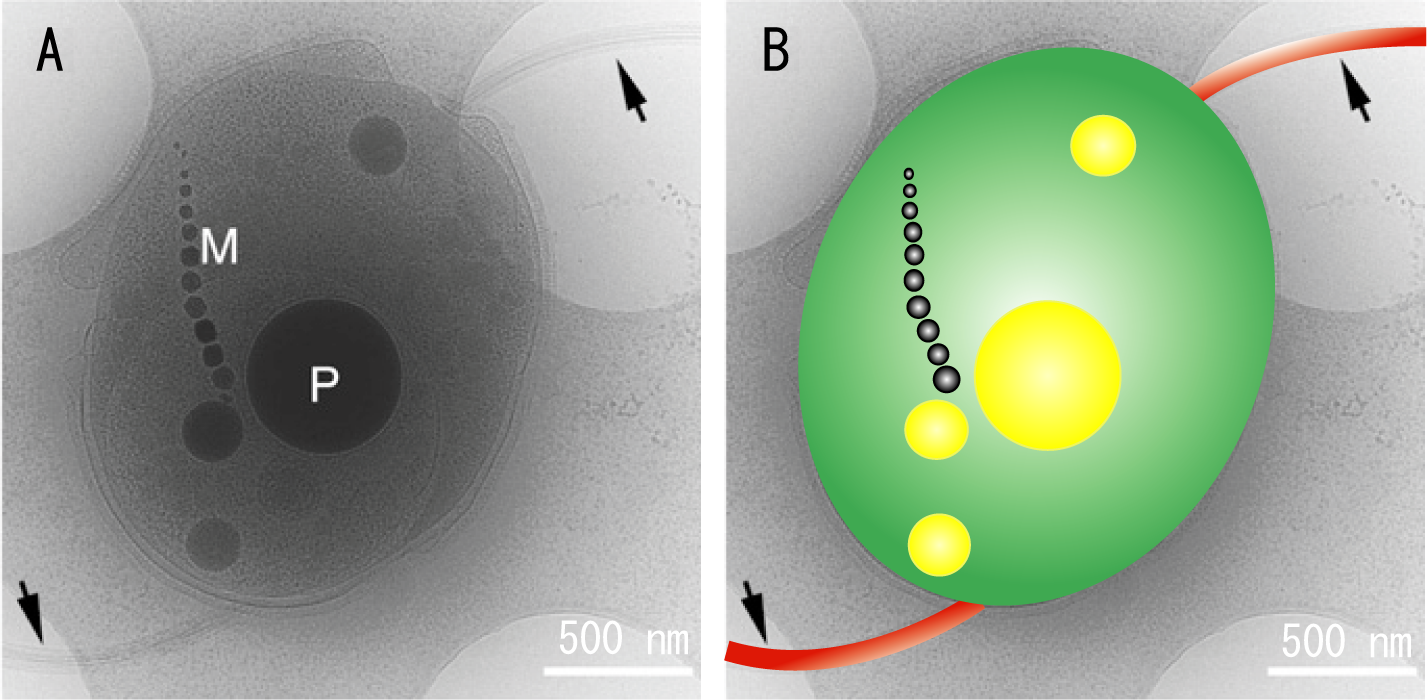
Figure 1
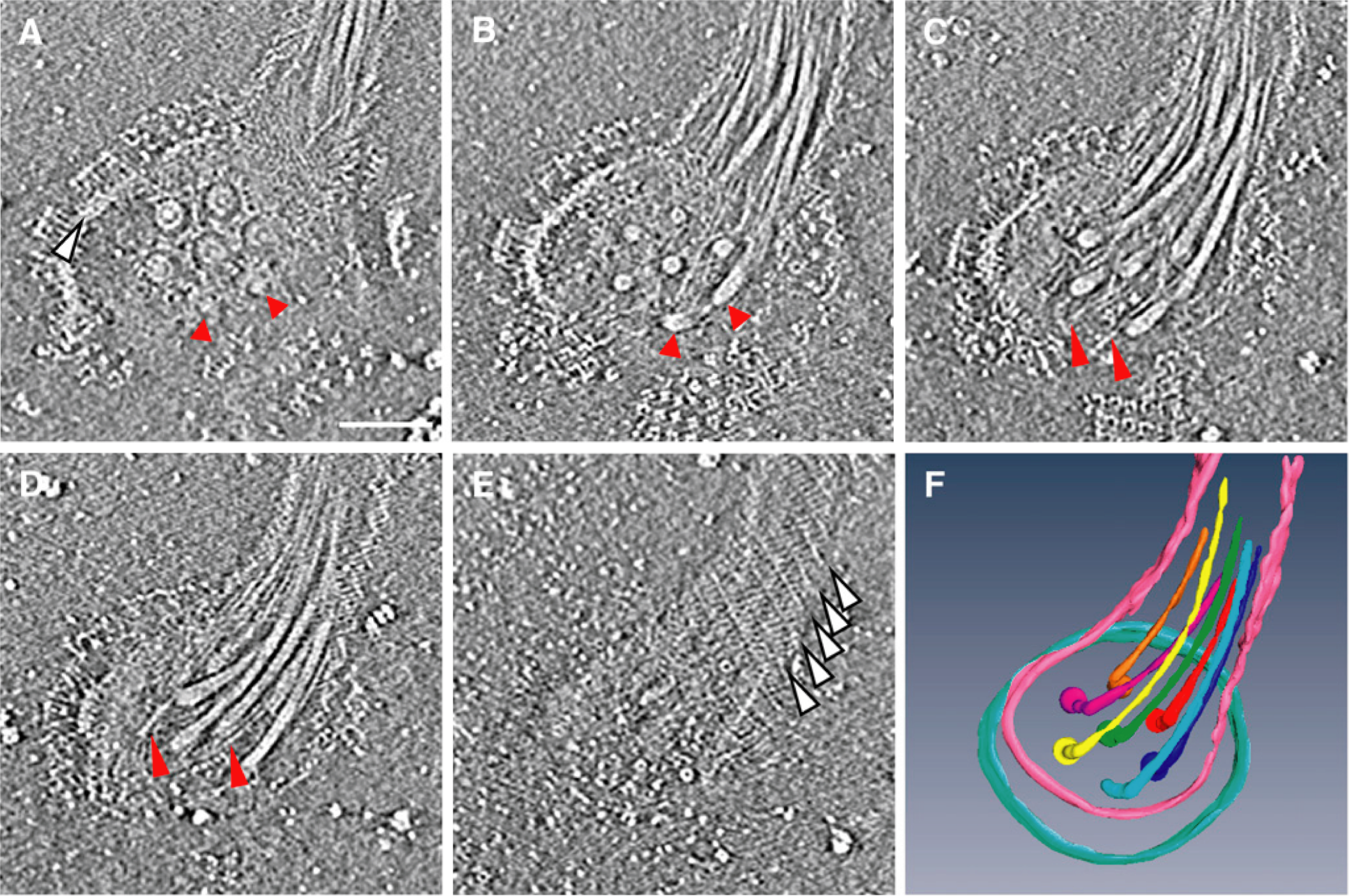
Figure 2
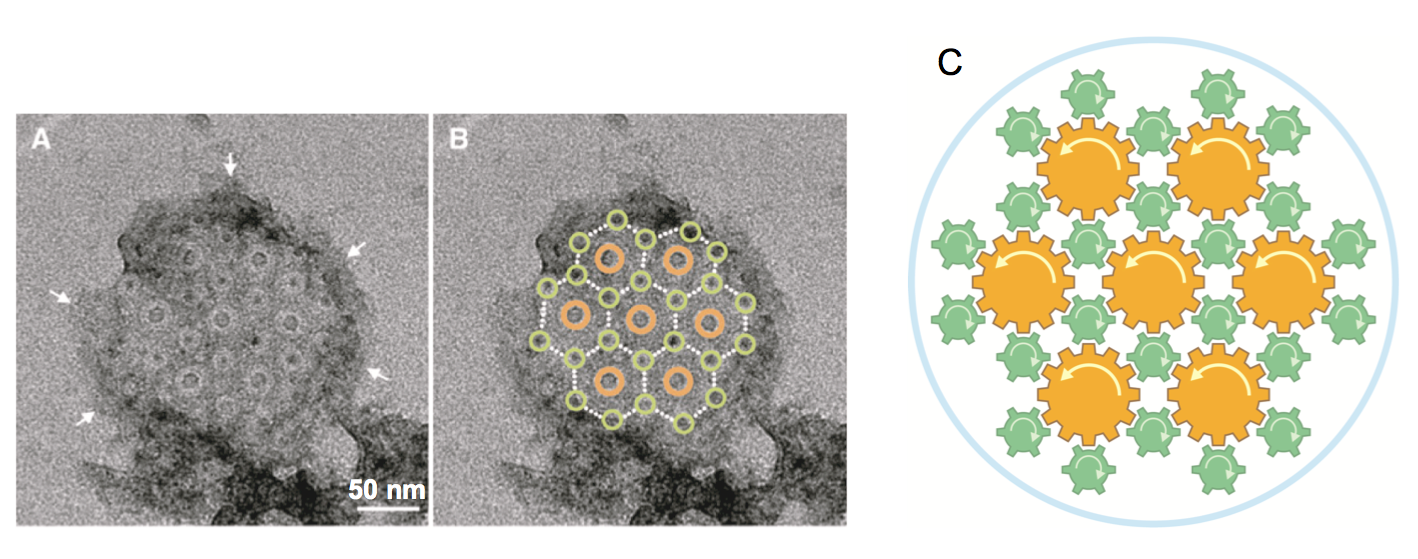
Figure 3
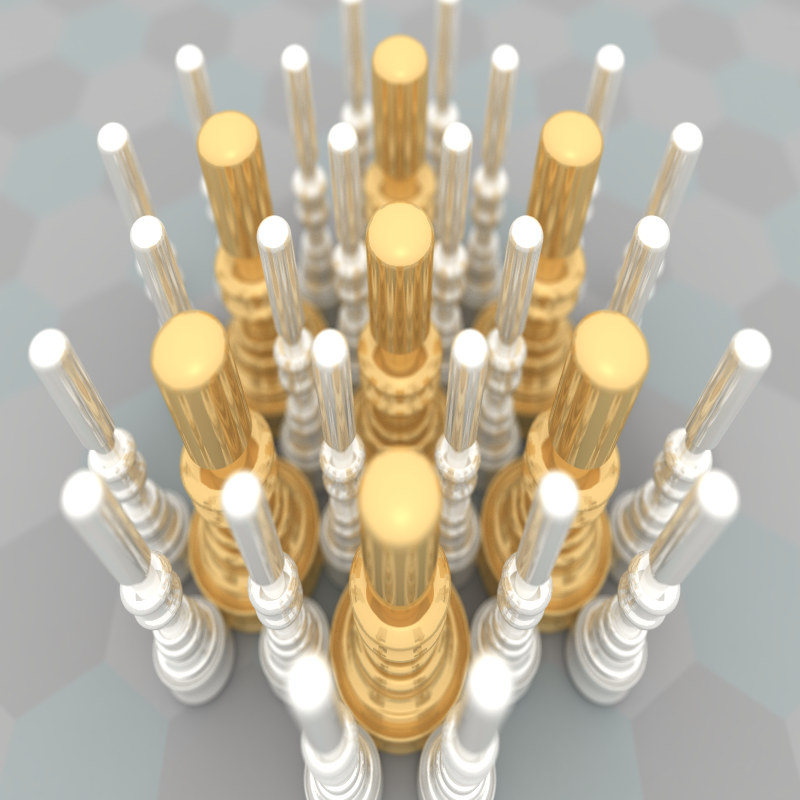
Figure 4
To read more about this important and fascinating research, please download the full research report entitled " Architecture of a flagellar apparatus in the fast-swimming magnetic bacterium MO-1 " available here at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) website.
Related link :
